Life is getting easier as generative AI tools help us complete day-to-day tasks, find new information, and work more productively.
Developers share how they perform code reviews via ChatGPT, designers ask the AI to offer them color palette ideas, and sales managers even have dedicated AI tools for automated sales.
Today, we will explore the most popular conversational AI tools and models behind them, such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Meta’s LlaMa 2, Google Bard, and Claude. We will look into each tool’s pros and cons plus recommend which one to pick to boost your productivity for your next project.
The main mechanism of LLM-based AI tools
As for now, most people have heard of ChatGPT, and a big percentage have adopted this tool for routine tasks, quick questions, or brainstorming. But how does this and similar models work?
Chatbots like ChatGPT and similar are based on LLMs (large language models). Any text is broken into tokens that can be as small as a character or as big as a few words. These tokens are then decoded, meaning understood by the system, and encoded, meaning produced as a new text from the system.
In other words, AI tools recognize patterns in texts and work to predict the next token in the sequence based on the data sets it was trained with. As a result, any text produced by generative AI is a set of pattern predictions token by token as AI makes its way through finding common associations between words and phrases.
For example, ask ChatGPT or any similar tool about cross-platform app development. The data sets the tool learned commonly have cross-platform, Flutter, and React Native in one text, so the AI will build a response containing these notions.
Let’s now move on from theory to practice and explore the best generative AI tools to assist you with software development or any other project.
OpenAI’s ChatGPT
ChatGPT, or its current version ChatGPT-4, is a conversational generative AI model developed by OpenAI. While GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) is an AI model designed for natural language processing and understanding, ChatGPT is adapted for giving dialogue-like responses. ChatGPT is a chatbot, while GPT is a model behind it.
ChatGPT is the most popular generative AI chatbot, as it was the first one to hit the open market and let anyone try it. GPT is widely recognized as the most advanced and coherent generative AI model today as it can recognize a variety of tones and language nuances as well as come up with original texts of various styles, explain complex notions, come up with ideas, and even write code.
ChatGPT pros
ChatGPT is one of the most extensive generative AI models with over 175 billion parameters. It allows this chatbot to come up with comprehensive and diverse responses.
This LLM successfully writes simple code, finds mistakes, or performs code reviews. It can assist with junior-level tasks in programming. There are even cases of mobile apps fully written with ChatGPT-generated code!
The same goes for content creation, idea generation, and more — ChatGPT can generate basic responses and polish your content.
ChatGPT cons
ChatGPT is trained on the wide scope of Internet data, such as various web pages. You might be familiar with the diversity of opinions shared online and the lack of credibility in some sources. As a result, the output ChatGPT produces should be taken with a pinch of salt, especially when it comes to scientific information.
Based on our comparison of ChatGPT with other bots, we noticed that this tool gives longer but often less relevant answers, taking up space with generic statements.
Use GPT to explore new ideas, write and edit naturally sounding texts for social media, and write simple code.
Meta’s LlaMa
Meta releasing its own LLM LlaMa is big news. Why? It’s another generative AI model that can create human-like texts, similar to GPT. While using its chat functionality, you probably won’t notice much difference between LlaMa and ChatGPT.
However, it has one significant advantage for researchers and organizations: LlaMa’s API is available for non-commercial use. What does it mean? Developers can download LlaMa’s code and fine-tune it according to their needs. Plus, the model is much smaller as compared to ChatGPT, making it accessible for running on a regular computer.
For example, companies can teach LlaMa to create custom chatbots, rate customer satisfaction levels based on feedback, cluster leads, and much more. One tool for fine-tuning LlaMa with ease is Microsoft’s LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models).
LlaMa’s pros
LlaMa (current version LlaMa 2) is quite a powerful chatbot. Compared to ChatGPT, it provides a similar level of responses regarding content generation, data analysis, and similar tasks.
What’s more, LlaMA has a separate LLM called Code LlaMa. Programmers and business owners can use this model for code completion, debugging, and simply writing new code. It is trained on a massive 500 billion tokens of code and code-related data. So far, Code LlaMa knows Python, Java, Typescript, PHP, and other programming languages.
LlaMa’s cons
As for now, LlaMa doesn’t have a convenient bot-like interface you can access from a browser. To use LlaMa’s chatbot capabilities, you need to either download it to your desktop or access the model through the Hugging Face website.
Because LlaMa is a rather small model, it can only sometimes grasp various jargon, tones of voice, humor, specialized terms, etc.
Plus, based on our experience, when accessing this model through Hugging Face space, the bot tends to cut the answer mid-sentence due to what we suppose is character limitation.
Use LlaMa to tweak the LLM according to your needs and build your personalized chatbot.
Google Bard
PaLM (current version PaLM 2) is a language model introduced by Google that is powering a set of Google’s products, such as
- AI bot assistant Bard
- Medical chatbot Med-PaLM 2
- Cybersecurity analysis tool Sec PaLM
- Productivity tools in Google Workspace.
You can access PaLM through Google’s very own conversational chatbot, Bard, to get help with project management, design, and content development tasks.
PaLM’s Pros
PaLM-powered chatbot Bard provides coherent, informative answers to prompts. Bard can also code and perform various programming tasks based on Python, Java, C++, and JavaScript.
One significant advantage is that, unlike other LLM chatbots, Bard has access to the Internet and, as a result, can provide up-to-date information or consider current events when giving recommendations. ChatGPT has similar functionality, but only for paid accounts. Plus, from our experience, it takes longer for ChatGPT to generate an answer based on online research.
Bard is significantly more convenient than ChatGPT: while in ChatGPT, you need to manually write any little change you want to the text, like making it shorter, Bard has a set of edits where you can adjust the text with one click.
Additionally, you can choose between several draft options without asking the bot to rewrite the answer.
PaLM’s Cons
Because PaLM and its chatbot Bard is a newer tool that Google marks as “an experiment,” it might not boast a well-established conversation flow and a high level of fine-tuning.
Use PaLM to get bot responses including the most current information and events.
Claude 2
Claude is a conversational chatbot created by a company called Anthropic. Claude is not just another LLM model to compete with GPT — Anthropic decided to create a safer, more secure AI.
Claude 2 is a large language model that powers the chatbot called Claude. Interestingly enough, Anthropic was founded by OpenAI’s ex-employees.
Claude 2 model is already integrated into a productivity tool Notion and Quora’s AI bot Poe.
Claude 2’s pros
Claude 2’s main focus is safety: this chatbot doesn’t engage in any conversations that can be a source of illegal activity information or provoke the chatbot to give discriminatory answers. How did Claude’s development achieve this?
The developers trained this LLM on the United Nations Declaration of Human Rights and Apple's terms of service. As a result, the model can differentiate offensive, inappropriate, or hateful statements. The team calls this method “Constitutional AI”. Additionally, the development team also provoked Claude to give offensive answers to block out these patterns.
Claude 2’s cons
As for now, Claude 2 is in an open beta version. It means that the model is not yet polished, and you shouldn’t expect high response speed or incredible accuracy. Sometimes, the bot can refuse to answer your question if you try to incline it to be offensive or ask something too hard.
Use Clause 2 to interact with a chatbot in a safe space and be sure of the political correctness and ethicality of the content you get from the AI.
Bottom Line
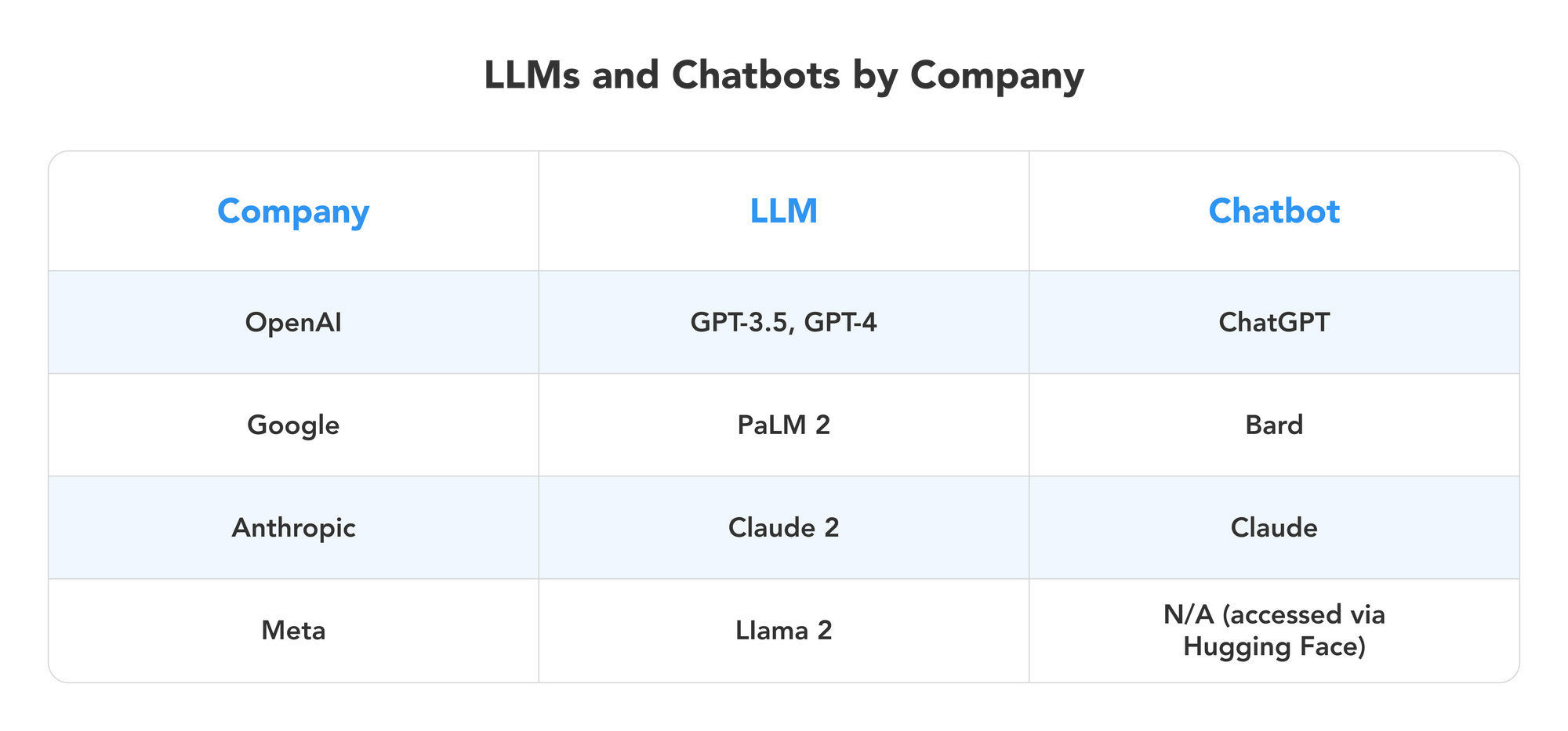
In the realm of generative AI tools, our daily lives are being transformed, with each tool offering unique advantages and use cases:
- OpenAI's GPT: A versatile chatbot and language model with over 175 billion parameters, ideal for tasks ranging from code writing and content creation to idea generation. ChatGPT is the go-to choice for natural and coherent text generation.
- Meta's Llama 2: LlaMa 2 presents a powerful chatbot, offering capabilities comparable to ChatGPT. It stands out for its API availability for non-commercial use, allowing developers to fine-tune it for specific needs. Additionally, LlaMa includes Code LlaMa, a code generation model suitable for programmers and businesses.
- Google's PaLM: Google's PaLM, employed in the Bard chatbot, offers up-to-date and informative responses. It's particularly useful for project management, design, and content development tasks. Bard provides a high level of convenience with quick text adjustments and internet access to current information for all users.
- Anthropic's Claude 2: Claude 2 prioritizes safety, distinguishing itself by preventing illegal or discriminatory responses. This chatbot's training on the United Nations Declaration of Human Rights and Apple's terms of service makes it a reliable choice for secure, ethical conversations.
These generative AI tools are poised to revolutionize how we work and interact with technology. Whether you seek natural language generation, content creation, or safety-conscious conversations, each tool has its strengths, and the right choice depends on your specific requirements.
To harness the full potential of AI for your projects, consider reaching out to Perpetio for expert guidance and customized solutions.





