Unfortunately, healthcare is not as accessible as we would like it to be. The physician shortage in the US, the high cost of insurance and medical services, and socioeconomic challenges all lead to limited access to healthcare for many.
One way to make medical services more accessible to the population is by introducing technology. Those who cannot see a medical professional in person can rely on online consultations if the case allows for it.
What’s more, telehealth technology allows space for more patients who need urgent in-person care by reducing the need for offline follow-up visits, hospital readmissions, routine visits, and more.
Telemedicine that combines video or audio calling, text chat, and AI capabilities can be a great replacement for long drives and queuing to ask a couple of questions. Plus, remote patient monitoring devices, like glucose meters and heart rate monitors, allow healthcare providers to track vital signs in real time.
This article explains how to make a telehealth product, including a mobile app and desktop version, which features such a product needs, and how much does it cost to build a telemedicine solution.
Telemedicine and Patient-Centric Healthcare
Patient-centric healthcare is all about focusing on the patient’s needs and preferences. It puts the patient at the heart of care, offering them choices in treatment and diagnostic methods, educating them about their health, and empowering them to be active decision-makers.
This approach isn’t just about treating a condition; it’s about treating the whole person, taking into account their unique circumstances, and ensuring they have the knowledge and options to make informed choices.
Telehealth plays a significant role in promoting patient-centric care by making medical services more accessible. 88% of physicians report that telemedicine has increased patient access to healthcare, particularly for those who previously faced barriers to care.
Whether patients live in remote areas or have mobility issues, telehealth bridges the gap, allowing them to receive medical attention without needing to visit a clinic in person.
Moreover, telehealth offers flexibility in how patients interact with their healthcare providers. They can choose the method that works best for them—whether it’s a video call, a phone conversation, or even a text message with a nurse. This not only provides convenience but also ensures that care is tailored to each patient’s needs and preferences.
Statistics also highlight telehealth's effectiveness: 57% of physicians use telemedicine to discuss lab results and treatment options, with the number rising to 70% among oncologists.
Among physicians, routine follow-up visits are the most common use of telemedicine technology (92% of surveyed physicians).
Additionally, most patients who had a telemedicine visit didn’t require an in-person follow-up within the same specialty for three months. This shows that telehealth can deliver effective care, reducing the need for frequent in-person visits.
Interestingly, a recent study by Epic Research revealed that most patients who had a telemedicine consultation didn’t need an in-person follow-up within the same specialty for three months.
Nearly 76% of patients who used telemedicine reported that it improved their access to healthcare services. This suggests that telemedicine can deliver effective care without further in-person visits.
Top Features of a Telemedicine Product
We have mentioned that video or audio calling and text chat functionality are the base of any telehealth solution. Let us share more details about the must-have telehealth app feature set.
To successfully implement telemedicine and meet the needs of both patients and medical professionals, it’s crucial to focus on key aspects like accessibility, usability, and comprehensive functionality. According to a survey, 92% of physicians identified ease of use as a vital factor in promoting patient access to telemedicine.
Cross-device compatibility, allowing access from both desktop and mobile devices, is also important, according to physicians. #
Additionally, avoiding mandatory application downloads and using login-protected patient portals can further ensure easy access.
Given these priorities, we recommend the following feature set for a telehealth product designed to cover all aspects of patient-doctor interaction. It is a real feature set we selected for a telemedicine platform we developed at Perpetio.
Developing a comprehensive telehealth solution involves catering to the needs of two primary user types: patients and healthcare providers. Typically, these apps are divided into distinct use cases for each group to ensure that both parties can interact as they would in an offline setting.
Below is a detailed feature set that addresses the specific needs of both patients and doctors, ensuring a seamless and effective telehealth experience.
Patient side
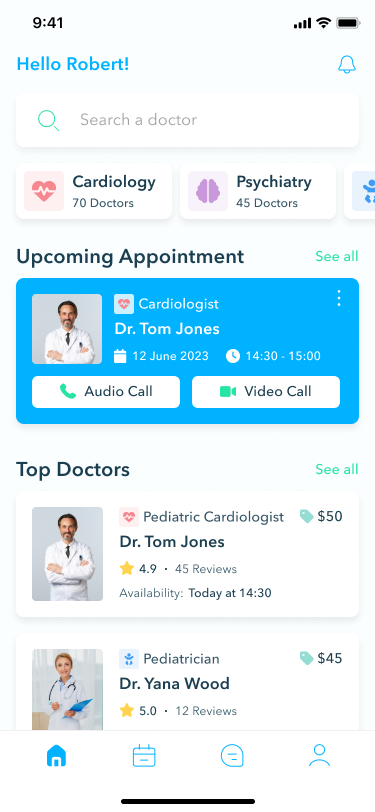
Home screen
The home screen serves as the starting point for all navigation. Here, users can search for a medical specialty or doctor by name, view upcoming appointments, see top-rated doctors, and select a medical department, such as cardiology or psychiatry. This central hub ensures that patients can easily find the information they need to manage their healthcare.
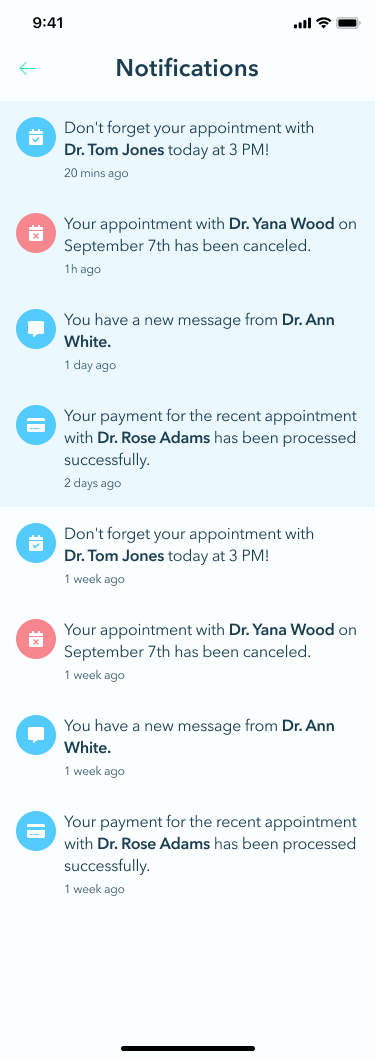
Notifications
Notifications play a key role in keeping patients informed. Whether it’s updates on appointment changes, payment statuses, or new messages from their doctor, timely notifications help patients stay on top of their healthcare, ensuring they never miss important updates.
Category search
For those with specific medical concerns, the category search feature allows users to browse specialists by department. Patients can sort doctors based on criteria like price and rating, making it easier to find a healthcare provider that fits their needs and budget.
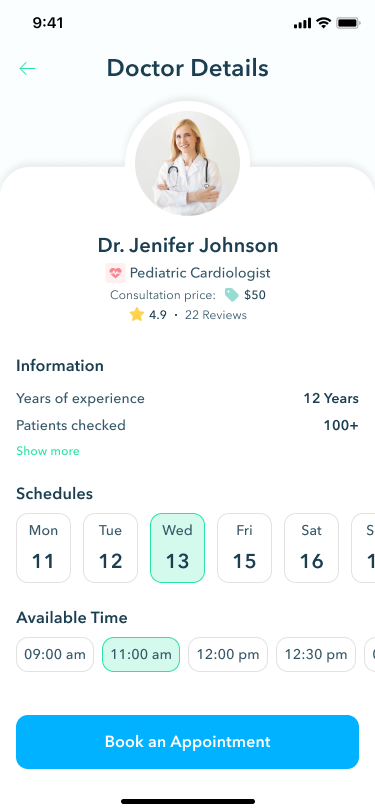
Doctor profiles
Doctor profiles offer detailed information, including specialization, consultation fees, patient reviews, years of experience, and available appointment slots. Patients can book appointments directly from the doctor’s profile, streamlining the process of connecting with healthcare providers.
Booking an appointment
Booking an appointment is simple and straightforward. Patients can select an available date and time, with integrated payment processing to handle appointment fees. If plans change, the app allows easy cancellation or rescheduling, giving patients flexibility and control over their healthcare interactions.
Your appointments
The "Your appointments" section provides a comprehensive overview of all upcoming and past appointments. Patients can view details such as date, time, and the doctor’s name, and they also have the option to cancel, reschedule, or message the doctor directly from this section.
Audio and video call functionality
Audio and video call functionality is essential for remote consultations. By integrating services like Agora, the app ensures smooth and reliable communication between patients and healthcare providers.
While 42% of patients prefer video consultations, 39% would rather go with audio only. So, it's crucial to let patients choose the option that is more comfortable for them.
After the consultation, patients can rate the experience and leave reviews, while automatic payment processing ensures a hassle-free transaction.
Messages
The messaging feature allows continuous communication between patients and healthcare providers. Whether it’s for follow-up questions, document sharing, or receiving prescription information, this feature enhances the overall patient experience by keeping the lines of communication open.
Personal profile
Patients can manage their personal and payment information in the personal profile section, which also provides access to help resources and account settings.
My anamnesis
The "My anamnesis" section offers patients a comprehensive overview of their medical history, including results and conclusions from previous consultations. This feature promotes informed decision-making and continuity of care.
Doctor’s side
Home screen
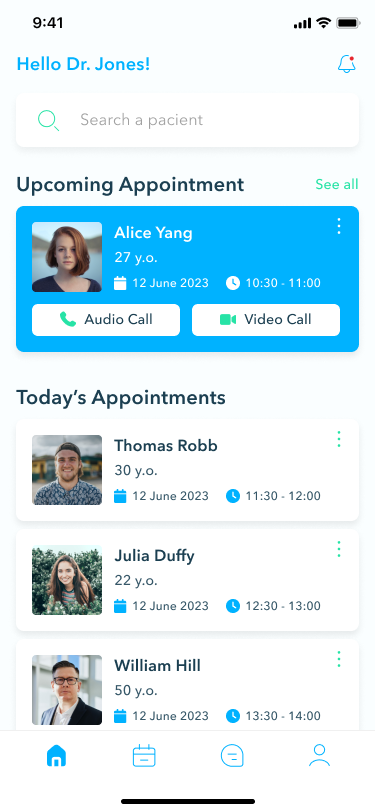
For healthcare providers, the home screen displays a quick overview of upcoming appointments, ensuring doctors are well-prepared for their sessions.
Appointments
The appointments section offers access to crucial details such as date, time, and patient information, with options to cancel appointments and exchange messages as needed.
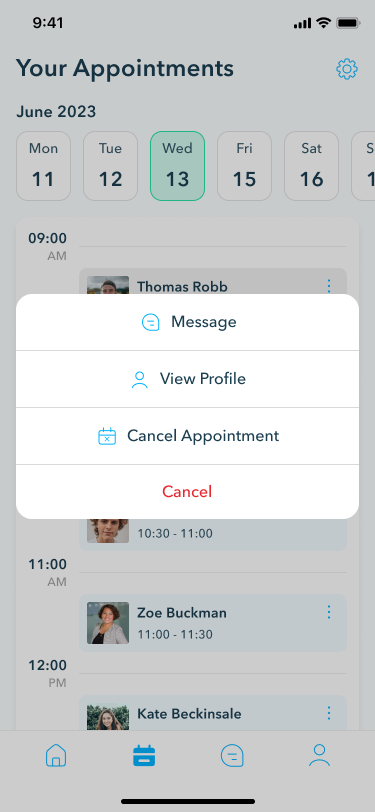
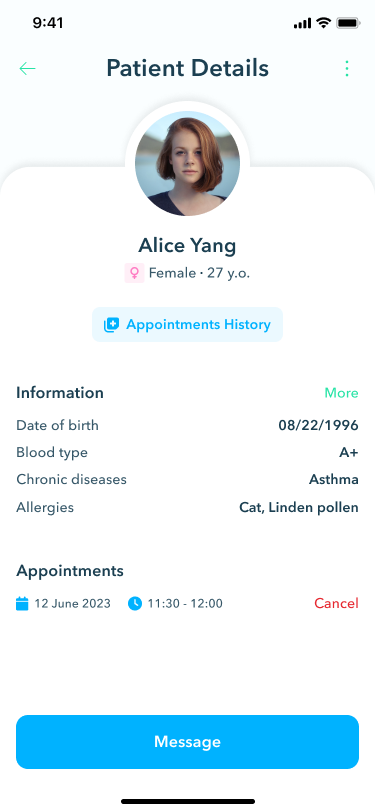
Appointment history
Maintaining thorough records is made easy with the appointment history section. Here, doctors can add details such as consultation reasons, findings, and prescribed medications.
Patient conclusion
After each consultation, doctors can document essential information in the patient conclusion section, summarizing the appointment's outcomes and recommendations. This feature ensures that important details are captured and easily accessible for future reference.
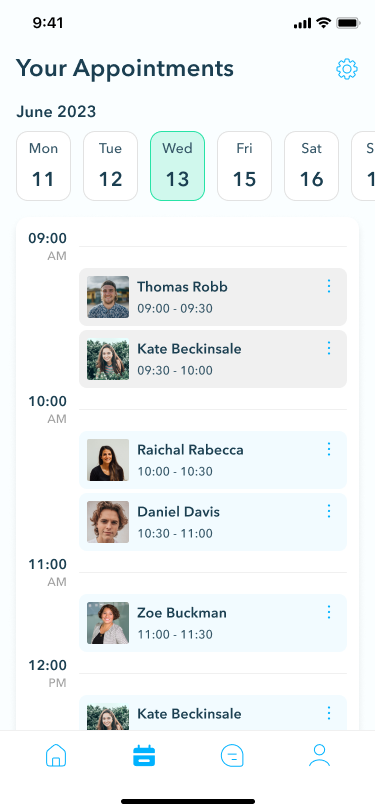
Work schedule
The work schedule feature allows doctors to manage their availability by searching for appointments on specific days. This functionality streamlines the scheduling process, enabling doctors to optimize their time and provide telehealth services more efficiently.
Video and audio call functionality
Reliable communication tools are essential for conducting remote consultations effectively.
Messages
The messaging feature further facilitates communication between doctors and patients, allowing for the exchange of information, addressing patient queries, and providing guidance.
These are the basic, must-have features that any telehealth solution requires to offer proper online medical consultations.
How to Use AI for Telehealth Solutions
AI is a powerful tool that can significantly enhance telemedicine apps by supporting three main functions:
AI-driven patient triage: Patients can input their symptoms into the app, answering a series of questions guided by AI. Based on the responses, the AI provides an assessment to help determine the best course of action, whether it's a virtual consultation, an in-person visit, a trip to the emergency room, or simply home care.
AI-enhanced remote patient monitoring: For patients with chronic conditions like diabetes or those recently discharged from the hospital, AI can monitor data from devices such as glucose meters or heart monitors. The AI algorithms detect any irregularities in the data, recommending whether the patient should schedule an online or offline appointment. In emergencies, the AI can alert the healthcare center immediately.
Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots offer patients a way to ask questions about their health, gain a better understanding of their symptoms, and learn more about their medications. This interaction provides patients with clarity and allows them to be more proactive and informed about their health, leading to more meaningful communication with their healthcare providers.
These features can help take some weight off the healthcare workers’ shoulders as patients can get first-line advice online from AI.
How to Build a Telemedicine Platform from Scratch
Take a look at the graph below. 77% of patients have access to smartphones for virtual healthcare visits, and 51% can join an online appointment via their computer.
To cater to the needs of both types of patients, we suggest developing two versions of a telemedicine platform: a mobile app and a desktop version of it.
To cater to the needs of both types of patients, we recommend developing two versions of a telemedicine platform: a mobile app and a desktop version.
Fortunately, getting both solutions isn't a hassle; with cross-platform development, it's straightforward to create an app that runs on iOS, Android, and desktops without needing to rewrite most of the code.
Here’s the telehealth development process based on our approach at Perpetio.
Step 1: Pre-planning and strategy development
Before diving into the development process, some essential questions need answers. First, it's crucial to partner with a reliable company that can guide you through the app-building journey.
Once you have chosen your development partner, whether outsourced or in-house, they will likely ask a few questions about
- your project’s technical and design requirements
- the app’s goals
- target audience (patients, healthcare professionals, both)
- preferred platforms (iOS, Android, desktop, or all)
- preferred development approach (native or cross-platform)
If these questions feel overwhelming, don't worry—having a basic idea of your telehealth solution is a great start. Your development team should offer tech consulting to help you make informed decisions. That’s how we operate at Perpetio.
After the pre-planning stage, you will receive a project roadmap or proposal outlining deadlines, milestones, budget, risks, and design and technical requirements. With this foundation set, it's time to begin the UI/UX design process.
Step 2: UI/UX Design
The design phase kicks off with thorough research rather than jumping straight into visual design. UI/UX designers use various research methods to ensure the product is competitive in the market, meets user needs, and provides a satisfactory experience.
Research approaches include studying the telehealth market, analyzing competitors, identifying the target audience's pain points, and creating user personas for both patients and doctors. Designers may also interview potential users to gain deeper insights.
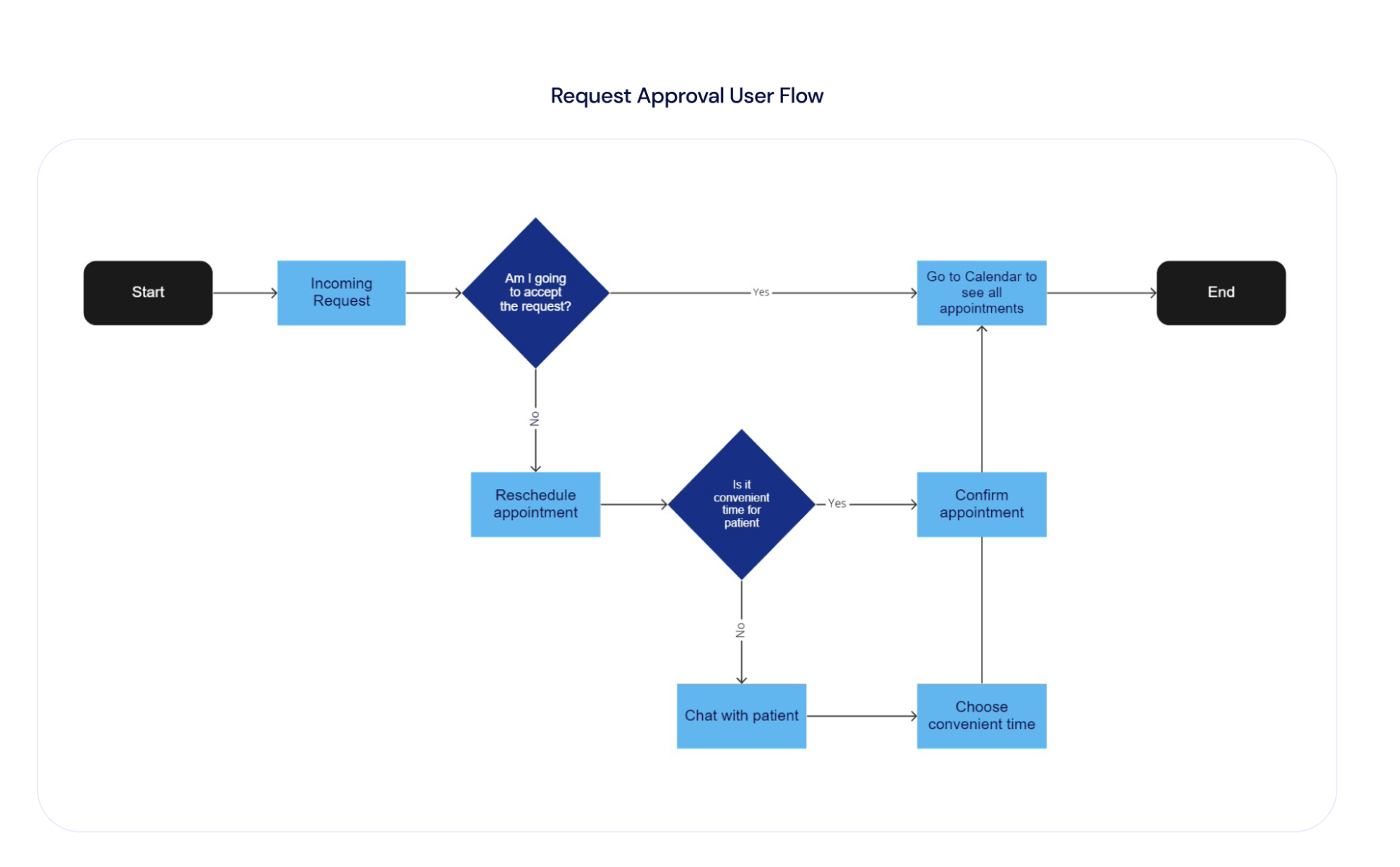
With this knowledge, designers create user flows for patients and doctors, followed by initial app prototypes, such as wireframes. Wireframes are basic prototypes that outline the application's pages, structure, and functionalities, including essential features like video calling and patient-doctor communication.
Wireframing allows for quick adjustments to the functionality before moving to high-fidelity, clickable prototypes. This stage is crucial for ensuring that both user types — patients and doctors — have seamless experiences.
Once the user flow is finalized, designers focus on the app's aesthetics, including fonts, colors, logos, and illustrations. It’s best to choose soothing colors that won’t distract or overwhelm the users when they are seeking medical help.
The design team will also make sure that the interface is inclusive and accessible: fonts are readable, text boxes are big enough, all the icons are clear, and the navigation is easy to understand. This is done so that users with different needs and levels of technology proficiency can get medical help online.
You will also receive a style guide to ensure consistent branding across the mobile and desktop versions of your telehealth platform.
Step 3: Development
After the UI/UX design phase is complete, it's time to dive into the development stage. This phase is crucial, as it involves translating designs into a fully functional telehealth app, complete with all the necessary features, such as video calling and two distinct user flows for patients and doctors.
One of the first decisions to be made is whether to go for native or cross-platform development. Native development involves creating separate apps for each platform, like iOS and Android, using their specific programming languages (Swift for iOS, Kotlin or Java for Android).
On the other hand, cross-platform development allows you to build an app that runs on both iOS and Android from a single codebase, using technologies like Flutter or React Native.
This approach is particularly useful for telehealth apps that need to be available on multiple devices, including mobile phones and desktops, without doubling the development effort. Cross-platform development can also speed up the process and reduce costs, making it an attractive option for projects with tighter budgets or timelines.
As development progresses, engineers work feature by feature, implementing designs, setting up the infrastructure, and integrating various services, such as payment gateways and secure messaging. The goal is to create a seamless experience across all platforms, ensuring that patients and healthcare providers can access the telehealth app from any device without any compromise in functionality or user experience.
Step 4: Testing
The development process doesn't end with the last line of code. Testing is a vital step to ensure your telehealth platform functions smoothly across all devices and user types.
The testing phase typically includes performance testing to evaluate load speed and responsiveness, security testing to prevent data leaks and ensure HIPAA compliance, and usability testing to provide a seamless user experience for both patients and doctors. This ensures that the video calling functionality works without glitches and that all features are intuitive.
After thorough testing and fixing any bugs, the team can confidently move on to the final stages: launch and maintenance.
Step 5: Launch and Maintenance
At Perpetio, we guide our clients through every step of the launch process. This includes obtaining necessary certifications, deploying the app on platforms like Apple’s App Store, Google Play, and desktop environments, and setting up monetization strategies.
A proper launch is crucial; skipping steps can undermine all the previous efforts. Post-launch, it’s essential to monitor the app’s performance and user satisfaction. Tracking metrics, reviewing feedback, and interviewing users help identify areas for improvement, ensure ongoing compliance, and guide future updates. This continuous monitoring is key to scaling your telehealth platform and ensuring long-term success.
With these steps, your telehealth app will be well-equipped to provide seamless and accessible healthcare services to patients, whether they’re on their phones or at their desktops.
The Technology Stack Behind a Telehealth Solution
Building a telehealth app that stands out requires selecting the right technology stack, ensuring it’s reliable, scalable, and user-friendly. Let’s dive into the key components and integrations that make this possible.
When it comes to mobile development, there are two main approaches: native and cross-platform.
Native development means creating separate apps for iOS and Android, using platform-specific languages like Swift for iOS and Kotlin or Java for Android. This approach is ideal for achieving top-notch performance and deep integration with device-specific features, which is crucial for telehealth functionalities like high-quality video calls and real-time notifications. Native apps often deliver a smoother user experience and can handle more complex tasks with ease.
On the other hand, cross-platform development uses a single codebase to build apps that run on both iOS and Android. Technologies like Flutter and React Native are popular choices here.
This method is particularly beneficial when you want to launch your telehealth solution across multiple platforms, including desktop, without duplicating the development effort.
In addition to mobile apps, many telehealth solutions require a desktop version to cater to healthcare providers who prefer working from a larger screen. For desktop applications, we often turn to technologies like Electron, which allows for the development of cross-platform desktop apps using web technologies. This ensures that your telehealth platform is accessible on any device, giving both patients and doctors the flexibility to choose how they want to communicate.
To ensure your telehealth app is as effective and user-friendly as possible, integrating the right third-party services is key. Here are some of the integrations we recommend:
HIPAA-compliant cloud storage: Given the sensitive nature of healthcare data, it’s vital to store information securely. Using a HIPAA-compliant cloud storage solution like AWS or Google Cloud ensures that all patient data is encrypted and stored according to the highest standards, protecting against data breaches and ensuring compliance with legal requirements.
Firebase for backend services: Firebase provides a reliable backend for your telehealth app, handling everything from authentication and cloud storage to real-time database management. It’s particularly useful for managing user data securely and efficiently, ensuring that the app remains responsive and dependable, even as your user base grows.
Twilio for SMS and notifications: Keeping users informed and engaged is crucial. Twilio can be integrated for SMS and push notifications, ensuring that patients and doctors receive timely updates. Whether it’s appointment reminders, prescription notifications, or follow-up messages, Twilio helps improve communication and reduce missed appointments.
Stripe for payments: Managing payments smoothly is another essential aspect of a telehealth app. Stripe offers a secure, user-friendly payment gateway that allows patients to pay for their consultations with ease. Supporting multiple payment methods, Stripe adds an extra layer of security, reassuring users about the safety of their financial transactions—especially important in healthcare.
Agora for audio and video calls: In telehealth, clear communication is everything. Agora is a leading service for real-time audio and video communication, offering high-quality calls that help patients and doctors connect as if they were in the same room. This integration supports not just video consultations but also real-time messaging, ensuring all critical information can be shared securely and instantly.
By carefully selecting the right technology stack and integrating essential services like Agora, Stripe, Twilio, and Firebase, your telehealth app will be not only functional and reliable but also intuitive and secure. This approach ensures that both patients and healthcare providers enjoy a seamless experience, no matter which device they’re using.
How Much Does It Cost to Develop a Telemedicine Product
When it comes to developing a telemedicine app, the costs can vary significantly depending on the specific features and platforms you want to include. It’s not a one-size-fits-all scenario—your choices in features, design, and development approach all play a crucial role in determining the budget.
For a basic telemedicine app with essential features like video calling, patient-doctor messaging, and appointment scheduling, the cost might range from $30,000 to $40,000. This would cover a simple, functional app that operates on either iOS or Android, offering users the fundamental tools they need for remote healthcare.
However, if you’re looking to create a more sophisticated telehealth solution, the costs will naturally increase. Integrating advanced features such as AI-driven patient triage, secure data management, and multi-platform support (including desktop versions) requires additional development time and resources.
Custom designs, high-quality user experiences, and complex functionalities like real-time notifications, HIPAA-compliant cloud storage, and cross-platform compatibility could push the cost upwards.
If you’re curious about how much your telemedicine app might cost, feel free to reach out to us. We offer free estimates to help you plan your project effectively and ensure you get the most out of your investment.